Colonialism Explained

What is Colonialism?
Colonialism is a system in which a powerful country takes control over another territory, often for economic gain and resources. This control is usually established through military force, political dominance, and cultural imperialism. The colonizing country imposes its own language, laws, and customs onto the colonized territory, often exploiting its natural resources and labor force for the benefit of the colonizers. Colonialism has had devastating effects on indigenous populations, leading to the loss of land, culture, and autonomy. The legacy of colonialism continues to impact many countries and societies today, as they struggle to overcome the lasting effects of exploitation and oppression.
2. Historical Context of Colonialism
Colonialism refers to the practice of establishing and maintaining colonies in distant territories by a dominant power for political, economic, and social control. The historical context of colonialism can be traced back to the Age of Exploration in the 15th century when European powers began to expand their empires through conquest and colonization. This period saw the rise of powerful empires such as the British, French, Spanish, and Portuguese, who sought to exploit the resources and labor of indigenous populations in regions such as Africa, Asia, and the Americas. The legacy of colonialism includes the exploitation and subjugation of native populations, the imposition of foreign political and social systems, and the lasting economic disparities that continue to impact these regions today.
Impact of Colonialism on Indigenous Cultures
Colonialism had a devastating impact on indigenous cultures around the world, as it resulted in the forced assimilation, exploitation, and suppression of indigenous peoples and their traditions. Indigenous languages, religions, customs, and ways of life were often prohibited, replaced with those of the colonizers. This led to the erosion of indigenous identities and knowledge systems, as well as the loss of land, resources, and autonomy. The trauma and legacy of colonialism continue to affect indigenous communities today, as they struggle to reclaim and revitalize their cultural heritage in the face of ongoing marginalization and discrimination.
Economic Exploitation under Colonial Rule
During colonial rule, economic exploitation was rampant as colonial powers sought to extract as much wealth as possible from their colonies. This often involved the forced labor of indigenous populations, the seizure of natural resources, and the establishment of trade monopolies that benefited the colonial powers at the expense of the local populations. Colonial economies were often structured to benefit the colonizers, with little regard for the well-being or economic development of the colonized people. This exploitation fueled the wealth and power of the colonial powers, while perpetuating poverty and underdevelopment in the colonies.
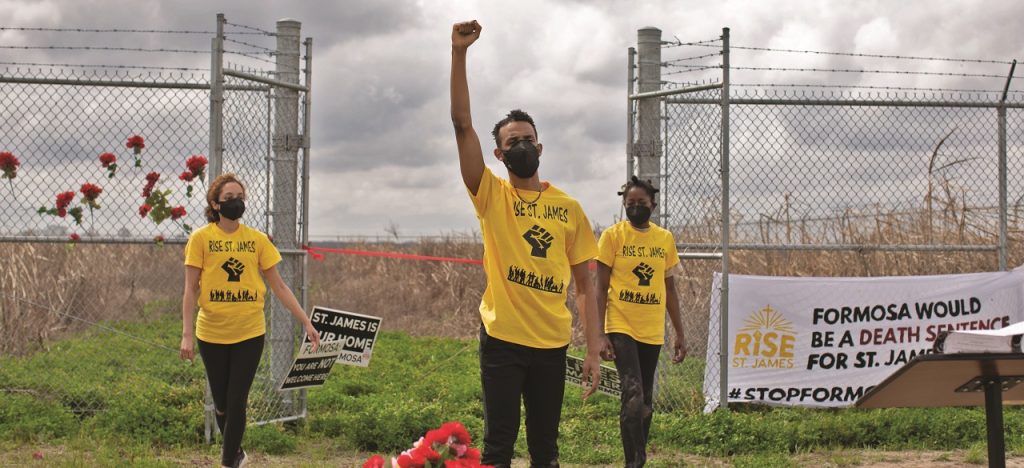
Political Control and Resistance
Political control refers to the ability of a government or ruling party to exert power and influence over its citizens through the use of laws, regulations, and social norms. This control can be exerted through various means such as censorship, surveillance, and propaganda. However, resistance to political control can also manifest itself through acts of civil disobedience, protests, and grassroots movements. This resistance can challenge the status quo and push for change, ultimately holding those in power accountable and ensuring that the voices of the people are heard. In this way, resistance serves as a crucial mechanism for maintaining a balance of power and fostering democracy within a society.
Social Hierarchies and Discrimination
Social hierarchies are systems of ranking individuals or groups based on perceived differences in power, status, and privilege. These hierarchies often lead to discrimination, as those at the top of the hierarchy may use their position to marginalize and oppress those lower down. Discrimination can take many forms, such as unequal access to resources, opportunities, and rights, as well as systemic prejudices and biases that perpetuate inequality. It is important to challenge and dismantle these social hierarchies in order to create a more equitable and just society for all individuals.
Legacy of Colonialism in Modern Society
The legacy of colonialism in modern society can be seen in the persistence of social and economic inequalities, as well as in the continued marginalization of indigenous peoples and communities. The effects of colonization, such as the exploitation of natural resources and the imposition of Western cultural norms, continue to shape power dynamics and perpetuate systems of oppression. Additionally, the legacy of colonialism can be seen in the enduring impacts of colonial policies on land rights, education, and healthcare, which have led to ongoing disparities and injustices for marginalized groups. Overall, the legacy of colonialism serves as a reminder of the need for decolonization and the recognition of historical injustices in order to create a more just and equitable society.
Decolonization Movements and Independence
Decolonization movements and independence struggles have been integral to the dismantling of colonial empires around the world. These movements have been driven by a desire for self-determination and autonomy, as well as a rejection of the oppressive and exploitative practices of colonial rule. Throughout history, colonized peoples have organized and mobilized to demand independence from their colonial rulers, often through acts of resistance, protest, and armed struggle. The successful decolonization of many countries in Africa, Asia, and the Caribbean in the 20th century is a testament to the power of grassroots movements and the resilience of those fighting for freedom and independence.
Repercussions of Colonialism on Global Economy
The repercussions of colonialism on the global economy have been profound and long-lasting. Many former colonies were left economically weakened and dependent on their colonizers for trade and resources. This has led to a legacy of inequality and underdevelopment in many regions of the world. Additionally, the exploitation of natural resources and cheap labor during colonial times has had lasting effects on the economies of these countries, contributing to ongoing issues of poverty and economic instability. The effects of colonialism can still be seen today in the unequal distribution of wealth and resources between former colonizers and their colonies, highlighting the lasting impact of colonialism on the global economy.
Post-Colonial Challenges and Opportunities
The post-colonial era presents both challenges and opportunities for formerly colonized countries. Challenges include the lingering effects of colonization such as economic dependency, social inequality, and cultural assimilation. These countries also face the task of rebuilding their political institutions and creating a national identity free from the influence of their former colonizers. However, the post-colonial period also offers opportunities for self-determination, cultural revival, and economic development. By embracing their unique histories and traditions, these countries can create a more inclusive and equitable society that is not defined by its colonial past. Ultimately, the post-colonial era is a time for these countries to assert their independence and forge a new path toward a brighter future.