The Rise of Fake News: Impact on Democracy and Society.
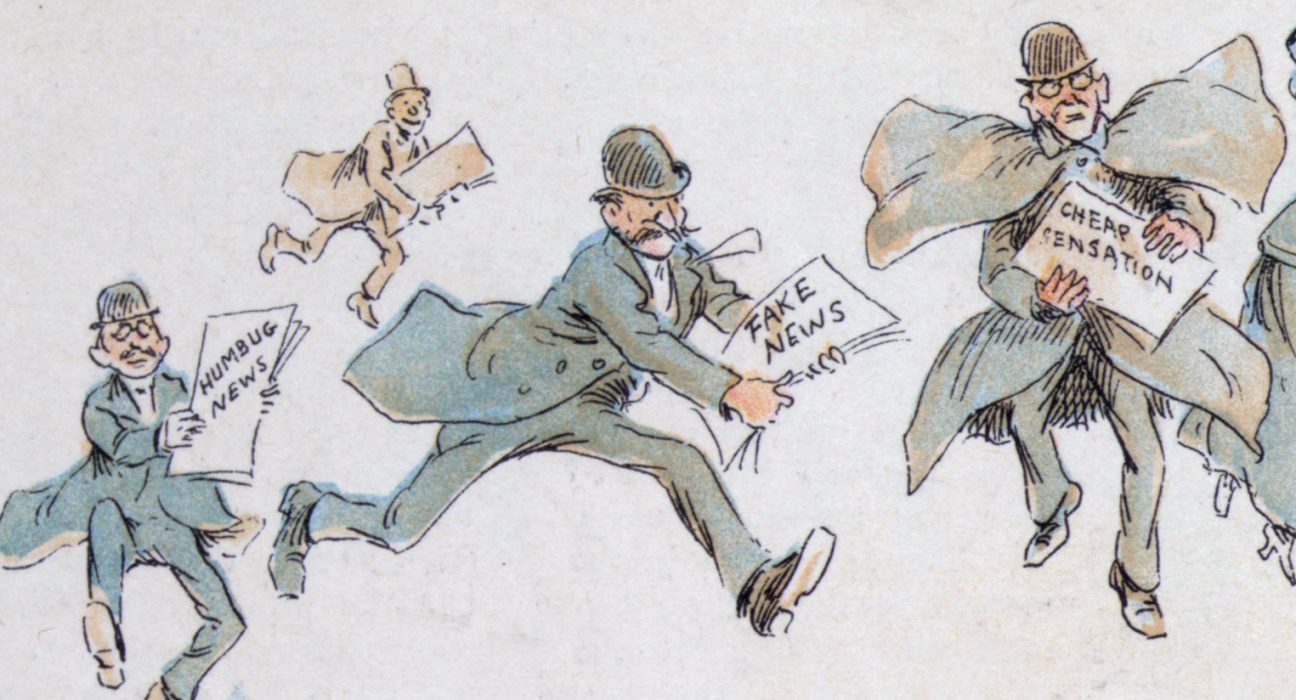

Introduction
The digital era has ushered in unprecedented access to information. However, this ease of access has also given rise to the phenomenon of fake news. Fake news, characterized by deliberately misleading or false information presented as factual, poses a significant threat to democracy and societal harmony. This article examines the rise of fake news, its impact on democratic institutions and social structures, and explores strategies to combat it.
Understanding Fake News
Fake news refers to fabricated stories designed to deceive, often created to influence public opinion or achieve political or financial gains. With the rapid dissemination of information on social media platforms, fake news can reach millions in a matter of hours, amplifying its effects exponentially.
The Emergence of Fake News
- Social Media and Algorithms:
Social media platforms use algorithms that prioritize engagement, inadvertently promoting sensational and often false content. - Decline in Traditional Journalism:
The shift to digital media has diminished the influence of traditional fact-checked journalism, making room for unverified and biased content. - Economic Incentives:
Clickbait headlines and viral fake news generate significant ad revenue, incentivizing the spread of misinformation. - Political Propaganda:
Fake news has become a tool for political actors to manipulate public opinion, polarize societies, and undermine opponents.
Impact on Democracy
- Erosion of Trust:
Fake news undermines trust in institutions such as the media, judiciary, and governments, creating a cynical and skeptical electorate. - Manipulated Elections:
Disinformation campaigns influence voting behavior, as seen in high-profile elections like the 2016 U.S. presidential race and Brexit. - Polarization of Society:
Fake news exacerbates ideological divides, fostering hostility between opposing groups and eroding social cohesion. - Threat to Free Speech:
The proliferation of fake news often leads to increased censorship, impacting freedom of expression and press.
Societal Consequences
- Spread of Misinformation:
Public health crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighted how fake news can endanger lives by spreading false medical advice. - Damage to Reputations:
Individuals and organizations can face irreparable harm due to unfounded rumors and fabricated scandals. - Loss of Critical Thinking:
Constant exposure to fake news diminishes people’s ability to discern credible sources from unreliable ones. - Rise in Hate Speech and Violence:
Fake news has incited violence and hate crimes, particularly against marginalized communities.
Combating Fake News
- Media Literacy Education:
Teaching individuals to critically evaluate information sources is essential to curb the influence of fake news. - Fact-Checking Initiatives:
Organizations like Snopes and PolitiFact play a critical role in debunking false claims and verifying information. - Regulation of Social Media Platforms:
Governments and tech companies must collaborate to create policies that prevent the spread of misinformation without infringing on free speech. - Promoting Reliable Journalism:
Supporting credible journalism through funding and public awareness campaigns can help restore trust in factual reporting.
Challenges in Addressing Fake News
- Rapid Spread of Information: Fake news travels faster than corrections, leaving lasting impressions.
- Bias Confirmation: People are more likely to believe information that aligns with their preexisting beliefs.
- Deepfakes and Advanced Technology: Tools for creating realistic fake content are becoming more accessible, complicating detection.
- Global Nature of Fake News: Coordinated disinformation campaigns often involve actors from multiple countries, making accountability difficult.
Legacy and Long-Term Impacts
Fake news has changed how societies consume information and trust public institutions. Its influence will likely grow as technology advances unless systematic efforts are made to counter it. Promoting an informed, critically thinking populace is the key to mitigating its effects.
Lessons Learned and the Way Forward
- Trust in institutions and media must be rebuilt through transparency and accountability.
- Collaborative international efforts are needed to tackle the global nature of fake news.
- Investment in AI and machine learning can aid in the early detection of fake content.
- Personal responsibility in verifying information before sharing is crucial.
Conclusion
Fake news is a pervasive issue that threatens democratic values and societal harmony. Addressing it requires a multi-pronged approach involving governments, technology companies, educational institutions, and individuals. By fostering media literacy, supporting fact-checking efforts, and prioritizing reliable journalism, society can combat the detrimental effects of fake news and uphold the integrity of democracy.